The collapse of three US regional banks – First Republic Bank, Silicon Valley Bank, and Signature Bank – marked some of the largest failures in the banking system since 2008. Central banks contained the “mini-crisis” earlier this year with forced interventions and the mega-merger of Credit Suisse and UBS. Despite the interventions, global banks still axed the most jobs since the global financial crisis.
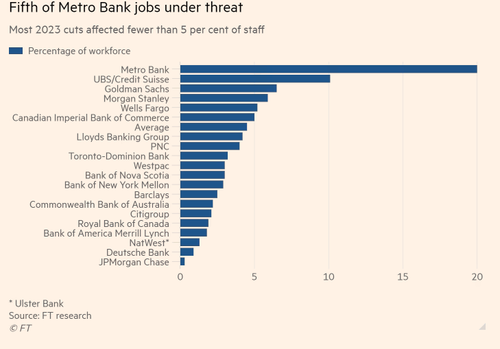
A new report from the Financial Times shows twenty of the world’s largest banks slashed 61,905 jobs in 2023, a move to protect profit margins in a period of high interest rates amid a slump in dealmaking and equity and debt sales. This compared with the 140,000 lost during the GFC of 2007-08.

“There is no stability, no investment, no growth in most banks — and there are likely to be more job cuts,” said Lee Thacker, owner of financial services headhunting firm Silvermine Partners.
FT noted that corporate disclosure data and its independent reporting did not include smaller regional bank cuts, indicating total job loss could be much higher.
At least half of the job cuts came from Wall Street lenders struggling with Western central banks’ most aggressive interest rate hikes in a generation.
The most significant cut of any single bank was at Switzerland’s UBS.
Morgan Stanley reduced jobs by 4,800, Bank of America by 4,000, Goldman Sachs by 3,200, and JPMorgan Chase by 1,000. As a whole, Wall Street cut 30,000 workers this year.
“The revenues aren’t there, so this is partly a response to overexpansion. But there is also a simpler explanation: political cost-cutting,” said Thacker.
Gaurav Arora, global head of competitor analytics at Coalition, warned: “We expect full-year 2024 to be a continuation of the story of 2023.”
Arora’s view of further turmoil aligns with our two recent notes: Banks’ Usage Of The Fed’s Bailout Facility Soars To New Record High and Large Bank Deposits Rise As Money-Market Outflows Accelerate, Small Banks Still Stressed.
“We see banks getting more conservative,” Arora concluded.




